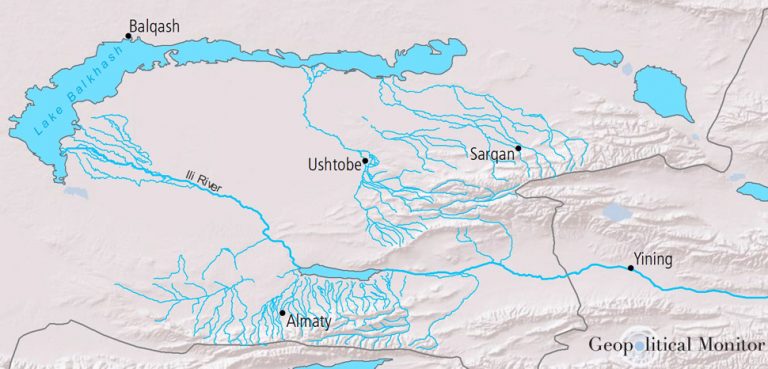
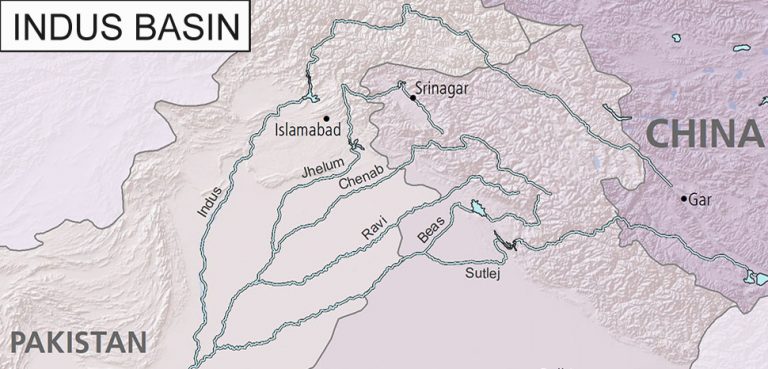
Manganese is a crucial, though often overlooked, metal that contributes significantly to modern industry. Overshadowed by more familiar elements like iron, copper, or nickel, manganese has special properties that are fundamental to the global economy. This article examines this essential commodity, scrutinizing its geopolitical and economic importance.
Manganese’s Properties and Applications
Manganese’s primary value lies in its ability to harden and enhance the durability of steel. Over 90% of manganese finds its purpose in steel production. It’s critical in construction, car manufacturing, and high-tech sectors, including aerospace and renewable energy.
Beyond steel production, Manganese’s versatile properties make it essential in other applications. It’s used in the creation of aluminum alloys where it improves corrosion resistance and the strength-to-weight ratio, a crucial factor in the aviation and transportation industries. Manganese also holds significant value in the production of batteries, particularly in the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) and portable devices. Manganese dioxide is used as a cathode material, contributing to a battery’s capacity, power, and stability.